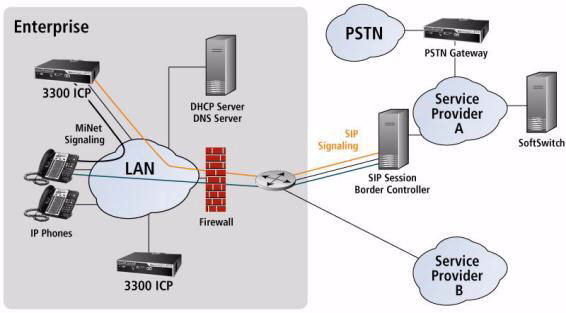
Service Providers offer SIP trunks that provide flexible and cost-effective WAN solutions for the 3300 ICP. SIP trunks allow the 3300 ICP to connect to the Service Provider through the SIP protocol over the IP network. (See the diagram below.) On the client side, SIP phones are starting to proliferate across the full spectrum of telephony vendors. The SIP Trunking solution provides basic feature functionality, billing capability, Emergency Services support, FAX support, and more. See the descriptions below for more information.

SIP Trunking supports 9-1-1 emergency service. The SIP Service Provider can be chosen as the outgoing emergency route. Ensure that the CESID information is programmed.
The Service Provider bills calls based on the peer connection to the 3300 ICP. The 3300 ICP records are created with a special SMDR tag entered in the SIP Peer Profile form. An SMDR tag can be enabled in the SIP Peer Profile form for outgoing and incoming calls.
Not supported over SIP at this time.
For Release 7.0, one restriction exists on a SIP-to-DISA call. During the call, the user cannot enter # followed by a remote number.
Communication between SIP Service Providers and the 3300 ICP can be configured to use either Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDN) or IP Addresses. The Network Elements form provides for the configuration of both for the SIP Peer. On the SIP Peer Profile form, the user can program the Local address as either a FQDN or an IP Address.
The SIP Trunking for Service Provider configuration supports FAX calls over G.711. Attempts to switch to T.38 are rejected, and the call continues as G.711. It is recommended that FAX machines be connected locally or through TDM to the 3300 ICP that is connected to the Service Provider through SIP trunks.
The SIP Satellite Office Solution configuration supports FAX calls over T.38. For more information on this configuration, see SIP Satellite Office. FAX routing can be configured through third party gateways using either prefix routing or COR routing. Prefix routing chooses a route based on a dialed prefix. COR routing chooses a route based on the COR group restriction on a route. If a particular device belongs to a COR group, it may be restricted from dialing out a particular route and then dials out the next route available in the route list.
FAX tone detection is used to disable the adaptive jitter buffer and echo cancellation to improve the reliability of FAX transmissions over IP networks. FAX tones can be detected in one direction (the TDM side) on the following types of calls: IP trunk to TDM, and SIP trunk to TDM. The Class of Service Option "Campon Tone Security/FAX Machine" is used to limit the codec selections to G.711 for Fax calls.
For incoming SIP calls that are tagged for Malicious Call, the 3300 records the Media IP address and port used remotely. As well, the SIP signalling information is captured. This information cannot be sent to the SIP Service Provider, but the information is recorded if needed.
Note: Malicious Call SMDR records are logged on the 3300 ICP. SIP endpoints cannot invoke Malicious Call Trace, but is it recommended that SMDR be enabled for SIP devices and gateways.
This option can be configured in the SIP Peer Profile form and may be necessary for the connection to the Service Providers. It allows periodic packets of audio when a one-way connection is detected to keep the NAT firewall open.
Each SIP Trunk can register with a registrar. The registrar is assigned using the Network Elements form.
SIP Trunking for Release 7.0 on the ICP 3300 is based on the following specifications.
RFC3261 - SIP Session Initiation Protocol
The 3300 ICP operates as a Back-to-Back User Agent.
It supports UDP, TCP, TLS transports.
Both SIP-URIs and TEL-URIs are accepted on incoming calls although only SIP-URI's are used for outbound calls.
The Options method used for link management.
The configuration allows for Outbound Proxy Servers.
Sending REGISTER messages is supported but incoming requests for registration are not.
RFC3262 - Reliability of Provisional Responses in Session Initiation Protocol
RFC4566 - Session Description Protocol
Supports G.711 A-law, µ-law, G.729a.
RFC3264 - An Offer/Answer model with SIP
RFC2976 - SIP INFO Method
RFC3311 - SIP UPDATE Method
RFC2833 - RTP Payload for DTMF Digits, Telephony Tones and Telephony Signals
RFC3325 - Private Extensions to the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) for Asserted Identity within Trusted Networks
Configuration allows for sending of P-Asserted-Identity and use of the Privacy header when privacy is requested.
RFC2617 - HTTP Authentication draft
RFC1321 - The MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm
RFC3263 - Session Initiation Protocol (SIP): Locating SIP Servers
Does not interpret "regexp" provisioned in NAPTR RR.
RFC2782 - A DNS RR for specifying the location of services (DNS SRV)
All Srv RR received are ordered jointly by priority and weight. For simplicity, the current implementation does not support server load balance information conveyed through the change of weight in SRV RR.
RFC4028 - Session Timers in the Session Initiation Protocol
Partial support, Session Timer is configurable.
RFC3515 - The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Refer Method
REFER may be received by the 3300 but will not be generated
RFC3891 - The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) "Replaces" Header
RFC3892 - The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Referred-By Mechanism
RFC3265 - SIP-Specific Event Notification
SUBSCRIBE message not supported.
Note: Within the 3300 ICP system, the characters #, *, @, and + have a special use. If these characters are used in a telephone name or number, they may not appear as expected when sent across a SIP Trunk.
Not supported at this time.
The system administrator can select from Always Active, Disabled, or Auto-Detect/Normal for SIP Trunks using the Network Elements form.
