Remote Directory Number Synchronization uses SDS to distribute the telephone directory entries to all the element databases in a network or cluster. In a network or cluster that uses Remote Directory Number (RDN) Synchronization, any telephone directory entries that you add, modify, or delete at an element (3300 ICP system) though the System Administration Tool are automatically distributed to the other elements. The updates are distributed to the other elements in the network or cluster via System Data Synchronization (SDS). In this mode, you can also configure device resiliency from the System Administration Tool (see Embedded Resilient Device Support for details).
If any elements in a network or cluster have MCD Release 4.1 or later software, all elements must use RDN Synchronization. If all elements in a network or cluster have MCD Release 4.0 software, all elements can use either RDN Synchronization or OPS Manager. If any elements in a network or cluster have pre-MCD Release 4.0 software, all elements must use OPS Manager.
Note: All elements within the same network or cluster that use SDS must be configured with the same telephone directory method.
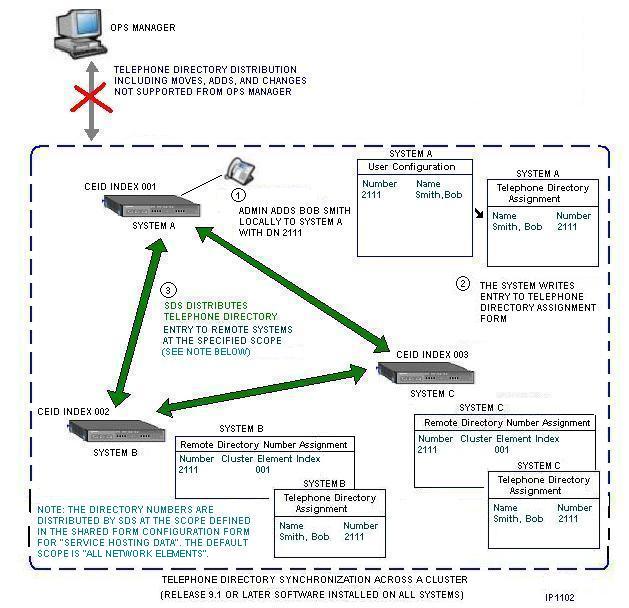
The following graphic illustrates how the telephone directories are synchronized across a cluster using RDN Synchronization.

The following table identifies the forms that are updated
with a new telephone directory entry. Both Element A and Element B support
RDN Synchronization, are sharing data, and the Telephone Directory form
is being shared at the "All 3000 ICP" scope. If you add a new
entry through the User and Device Configuration form on Element A, the
entry is written into the databases of both Element A and Element B and
recorded in the following forms:
|
Forms on Element A |
DN listed in form |
Forms on Element B |
DN listed in form |
|
User and Device Configuration |
Yes (local number) |
User and Device Configuration |
No (remote number) |
|
Telephone Directory (shared at "All 3300 ICP" scope) |
Yes |
Telephone Directory |
Yes |
|
Remote Directory Numbers |
No (local number) |
Remote Directory Numbers |
Yes (remote number) |
RDN Synchronization is subject to the following requirements:
The network or cluster can contain only 3300 ICPs.
All elements in the network or cluster must have MCD Release 4.0 or later software.
RDN Synchronization is mandatory with Release 4.1 and later software.
Note: To migrate a network or cluster to RDN synchronization, refer to Mitel Knowledge Base article 09-3070-00008, "Migrating to RDN Synchronization via SDS," on Mitel Online.
RDN Synchronization is subject to the following limitations:
You cannot
synchronize an element that has pre-MCD Release 4.0 software with an element that has MCD Release 4.0 or later software and is using RDN Synchronization.
start sharing data from an element that is using RDN synchronization to an element that has pre-MCD Release 4.0 software.
start sharing from an MCD Release 4.0 element that is using OPS manager to for telephony directory management to an element that is using RDN Synchronization.
distribute a directory entry to a specific list of elements. With RDN synchronization, SDS shares directory entries at the specified sharing scope. All elements within the specified scope, share the directory entries. Unlike OPS Manager, you cannot distribute a directory entry to a specific list of elements.
Do not downgrade an element in the RDN Synchronized network from MCD Release 4.0 or later software to pre-MCD Release 4.0 software. This downgrade is not supported and will result in shared data updates on the element that is running pre-MCD Release 4.0 software.
It is possible to return an RDN Synchronized network back to being a non-RDN Synchronized network. However, this process is not recommended or supported. You must restore a non-RDN Synchronized database on every node in the network. Then, you will need to re-enter any configuration changes that were made after the migration to RDN Synchronization took place.
You cannot restore a non-RDN Synchronized database to an element that is RDN Synchronized.
After migrating an element to RDN Synchronization, you must download an updated version of the Import/Export Spreadsheet. And, any data that you exported prior to the migration cannot be re-imported.
You cannot export data from a non-RDN Synchronized system and then import the data into an RDN Synchronized system with the exception of the IP Consoles form. You can export data from the IP Consoles form on a non-RDN Synchronized system and then import it into an RDN Synchronized system system.
By default, non-prime DNs will be hosted on the same element as the associated set. For example, consider a set with DN 1111, hosted on element A. If the administrator programs button 3 to be a single line with DN 1112, then DN 1112 will default to being hosted on element A.
RDN Synchronization differs from traditional telephony directory management in the following ways:
By default, telephone directory entries are shared as General System Data at the "All 3300 ICPs" scope. You can edit any telephone directory entry from any element that is included in the SDS sharing scope assigned to the Telephone Directory.
There are two new restrictions that apply to Telephone Directory form:
If the directory number (DN) for an entry is a device DN, you cannot change it to a non-device DN (ARS string or group feature DN).
If the DN for an entry is a non-device DN, you cannot change it to a device DN.
An "Add" operation that you perform from the User and Device Configuration form always creates a new user entity, even if a user already exists with the same name.
In forms that allow you to add or modify the directory name, such as the Telephone Directory form, the first name and last name can be up to 64 alphanumeric characters in length.
The Remote Directory Numbers form becomes read-only and the Add, Change, and Delete buttons are no longer available in this form. View is available instead.
The Departments and Locations forms do not display the Index column after the migration, so you can no longer search by Index number. However, you can search on department name or location in these forms when the system has been dimensioned to support large lists in the database.
The list of forms in the SDS Form Sharing form is modified:
The "General System" group of forms contains the Telephone Directory form.
The "User Definition" group of forms contains entries for the following data: Departments, Locations, User and Device Configuration - User Attributes, User Authorization Profiles.
"Service Hosting Data" is a new group of forms that allow the sharing of local-only directory numbers, hosted system data, and hosted user data.
You can configure device resiliency from the User and Device Configuration form and IP Console resiliency from the IP Consoles form of the primary element. After migrating to RDN Synchronization, you cannot use OPS Manager to configure device resiliency.
Simultaneous changes to data records are not shared via SDS. If two administrators perform changes on the same data record at the same time, shared updates will not be generated and the data record will be different on both systems.