Automatic Route Selection (ARS) simplifies local and long distance dialing by automatically selecting the most convenient and cost-effective route, and by inserting and/or deleting digits for proper routing.
When a route that is not the least expensive is selected, you hear ARS Expensive Route Warning Tone. When you hear the tone, you can either proceed with the call, Camp-on to the least expensive route, request a Callback from the least expensive route, or abandon the call.
Automatic Route Selection (ARS) is a standard feature which routes trunk calls based upon:
route availability, where a route is defined as a collection of similar trunks within a trunk group
cost, when more than one route exists
toll restriction, that is whether the caller is allowed to make such a call, and if so, on what facility.
Automatic Route Selection functions without input from the user. ARS is not dependent on a fixed numbering plan.
Advanced Automatic Route Selection is an optional feature that provides automatic selection of routes based on the time of day/week (least cost routing).
Automatic Route Selection is compatible with any numbering plan employed by any public network. To take full advantage of the toll control application of ARS, however, you must understand the numbering plan used by the public network.
ARS digits can be specified with leading digits as well as dialed digits. These digits can be listed explicitly, or you can use "wildcards" to specify predefined variables for a given ARS digit:
N or n specifies a digit between 2 and 9 inclusive.
X or x specifies a digit between 0 and 9 inclusive.
Y or y specifies a digit between 0 and # inclusive.
To view examples of ARS entries, refer to ARS Programming example.
North American Numbering Plan
The North American numbering plan enables any subscriber in a public network to connect to any other subscriber in the network. The North American numbering plan assigns each subscriber a unique digit string of a maximum of 10 digits:

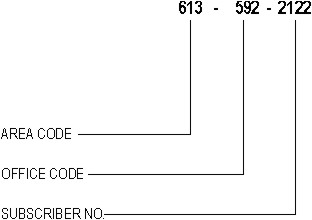
The area code defines a geographic telephone area. The office code identifies a central office (CO) within the area. And the subscriber number identifies a subscriber of the CO.
Local calls are generally placed by dialing the office code and the subscriber number - for example, 555-2122. In some areas, however, local calls are placed by dialing the area code, office code, and subscriber number - for example 613-555-2122.
Tolls calls are generally placed by dialing the prefix digit 1, the area code, office code, and subscriber number - for example, 1-613-555-2122. In some areas, however, toll calls between two subscribers within the same area code are placed by dialing the prefix digit 1, the office code, and the subscriber number - for example, 1-555-2122.
Some telephone numbers are reserved for services - for example, 411 for directory assistance. These service numbers do not conflict with area or office codes.
Finally, a subscriber can dial the digit 0 to call the operator.
ARS adheres to the assigned Class of Restriction (COR) values.
You cannot
Camp-on to or request a Callback
from the ARS least expensive route:
- if the trunk in question is programmed for Overlap Outpulsing
- if all of the least expensive route trunks are out of service.
SUPERSET 410, SUPERSET 420, SUPERSET 430, SUPERSET 4015, SUPERSET 4025, SUPERSET 4125, and SUPERSET 4150 telephones; 5010 IP Phone, 5020 IP Phone, 5140 IP Phone, 5207 IP Phone, 5212 IP Phone, 5215 IP Phone, 5215 IP Phone (Dual Mode), 5220 IP Phone and 5220 IP Phone (Dual Mode), 5224 IP Phone, 5230 IP Phone, 5240 IP Phone, 5235 IP Phone, 5304 IP Phone, 5312 IP Phone, 5324 IP Phone, 5320 IP Phone, 5330 IP Phone, 5340 IP Phone, 5360 IP Phone, Navigator, and 5560 IPT:
To respond to ARS Expensive Route Warning Tone:
Do one of the following:
To proceed with the call, wait two seconds.
To Camp-on to the least expensive route, press Campon, Wait, or I Will Wait within two seconds.
To request a Callback from the least expensive route, press Callback or Call Me Back and hang up.
To abandon the call, hang up within two seconds.
2500, SUPERSET 401, SUPERSET 401+, and SUPERSET 4001 telephones; 5001 IP Phone, 5005 IP Phone, 5201 IP Phone, 5205 IP Phone, and 5302 SIP Phone; Symbol Wireless Phones:
To respond to ARS Expensive Route Warning tone:
Do one of the following:
To proceed with the call, wait two seconds.
To Camp-on to the least expensive route, dial the Camp-on Feature Access code within two seconds.
To request a Callback from the least expensive route, dial the Callback Feature Access Code within two seconds.
To abandon the call, hang up within two seconds.
