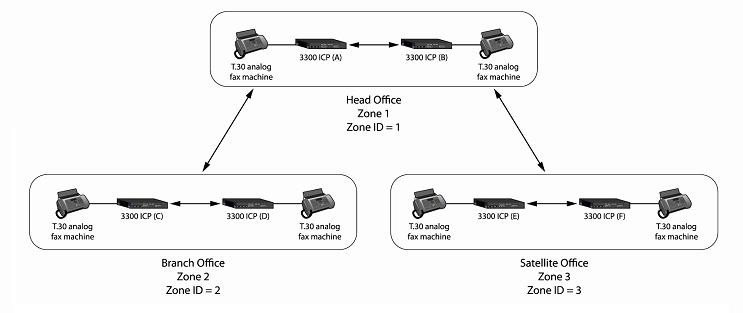
Draw a diagram of the zone topology for the FAX communication.
If possible, always route FAX communication over the IP network using T.38 signalling to reduce costs and ensure quality of service.
A FAX Relay (T.38) signalling session consists of a two FAX machines communicating across the IP network using T.38 protocol. The number of sessions is limited by the available system DSP II card resources. Refer to the Engineering Guidelines to calculate the number of T.38 signalling sessions available for each system in the network.
If there are not enough system DSP resources to allow you to route all FAX communication over the IP network using T.38 signalling, use G.711 pass through between FAX machines located within the same LAN (intra-zone), and use T.38 sessions between FAX machines that are located on the WAN (inter-zone).
Assign each zone a Zone ID and a Label.
Locate the 3300 ICPs in the appropriate zones. Typically, 3300 ICP systems that are located on the same LAN should be in the same zone. 3300 ICPs separated by the WAN, should be in separate zones.
The following figure shows a zone topology example:

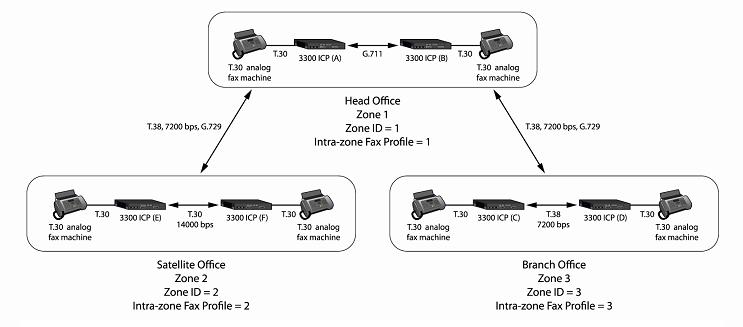
Define the settings for the Intra-zone Profiles and the Inter-zone Profiles.
The Inter-zone Profile defines the settings for FAX calls made between zones. An Intra-zone profile defines the settings for FAX calls made within a zone.
Identify the Inter-zone setting for FAX calls between the zones. See Fax Service Profiles for the possible settings.
Identify the Intra-zone settings for FAX calls within each zone.
The following figure shows a zone topology example with the FAX settings identified:
Record the zone data in tables (see examples below)
|
Network Elements Form |
||
|
Element Name |
Type |
Zone |
|
3300 ICP A |
3300 ICP |
1 |
|
3300 ICP B |
3300 ICP |
1 |
|
3300 ICP C |
3300 ICP |
2 |
|
3300 ICP D |
3300 ICP |
2 |
|
3300 ICP E |
3300 ICP |
3 |
|
3300 ICP F |
3300 ICP |
3 |
|
Inter-zone FAX Profile (applied between all zones in network) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Maximum FAX rate |
High Speed Redundancy |
Low Speed Redundancy |
ECM |
NSF Override |
NSF Vender Code Value |
Label |
|
7200 bps |
0 |
3 |
Disabled |
Disabled |
0 |
Inter-zone |
|
Intra-zone FAX Profiles (within zones) |
|||||||
|
Profiles |
Maximum FAX rate |
High Speed Redundancy |
Low Speed Redundancy |
ECM |
NSF Override |
NSF Vender Code Value |
Label |
|
1 |
--- |
--- |
--- |
--- |
--- |
--- |
G.711 |
|
2 |
14000 bps |
0 |
3 |
Disabled |
Disabled |
0 |
T.38 |
|
3 |
7200 bps |
0 |
3 |
Disabled |
Disabled |
0 |
Inter-zone 3 |
|
Network Zones |
|||
|
Zone ID |
Intra-zone Compression |
Intra-zone FAX Profile |
Label |
|
1 |
No |
1 |
Head Office |
|
2 |
No |
2 |
Branch Office |
|
3 |
No |
3 |
Satellite Office |
Identify and purchase the required resources:
Each FAX machine that uses T.38 signalling requires a "FAX over IP (T.38) License" on its host 3300 ICP.
Typically, each FAX machine that uses T.38 signalling to communicate with a FAX machine in a different zone should also be assigned a compression license. See IP Networking/XNET Compression for details.
Ensure that the system has enough DSP resources to support the required number of T.38 licenses and compression licenses (refer to the Engineering Guidelines for details).
To support FAX Relay (T.38) signalling, each 3300 ICP system requires the DSP II (PN 50005751) card. There are eight DSPs on a DSP II card. Each DSP supports eight T.38 channels, so the DSP II module supports up to 64 T.38 channels.
Proceed to Configure FAX Over IP Support.