Buttons in the Network Elements form allow you to
bring elements into a data sharing community of elements, and then
synchronize the shared data at one or more elements with the data on the local element.
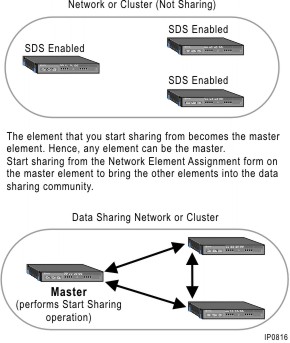
The following graphic illustrates the Start Sharing process:

The Start Sharing button begins sharing the specified data from the local (master) element with the selected remote (slave) elements at the defined scope. After you enable sharing, the data that you identified in the SDS Form Sharing form will be shared among the selected elements. Then, if a record is added or modified in a shared form of one of the elements, the update will be made automatically in the databases of the other elements. The Start Sharing operation only synchronizes the Network Element data, Cluster Elements membership data, and other internal SDS related data across the elements. It adds the element to the sharing community (member elements) and begins the sharing of data at the specified scope.
The Sync button allows you to synchronize the shared data on the local element with one or more remote elements. Before you can perform a Sync operation the remote elements must already be sharing data with the local element at the desired scope.
A Sync operation consists of the following stages:
All System Administration Tool, Group Administration Tool, Desktop Tool, and MiXML sessions are blocked from accessing the elements.
Each of the remote (slave) elements collects the shared data from its forms.
All the shared data from the remote elements is written to the local (master) element to create one merged master database. If new records are discovered on the remote elements, you can configure the system to add these records to the merged master database. Only different records from the remote nodes are added into the master database. If the same record exists on the elements but the field contains different data, the records from the forms are not added but are overwritten with the data from the master element.
The databases on the remote elements are then overwritten with the master database from the local element.
Pending errors or pending shared updates to the remote nodes are removed from the local node because they will no longer be required (applies only to forms that have been selected for synchronization).
Any data updates sent from the other elements to an element involved in a synchronization will be rejected by that element and recorded as error on the master that sent the update.
Notes:
It's recommended that you provision data sharing from one master element in the network or cluster. If you provision data sharing from a master element, you can monitor distribution errors from that one master element. However, if data sharing is provisioned from multiple elements, then you must log in separately to each element and check for distribution errors. An alarm is generated if distribution errors are present.
In Release 7.0, the system aborts an SDS synchronization operation after a system-wide total of 500 errors. The error threshold for an SDS Synchronization failure was increased from 5 errors per form in Release 6.0 to a total of 500 errors system-wide in Release 7.0.
If creating a new network or cluster, you must configure the elements to start sharing data and then synchronize the shared data of the local element (master) with the remote elements (slaves).
If modifying an existing cluster or network where the databases are already very similar, you may choose to just perform a Start Sharing operation. Depending on the number of records being synchronized, a synchronization operation can be time consuming and it may not be necessary if most of the data is identical. You can use the Form Compare tool to identify differences and then only sync those forms that are out of sync. If the Form Compare identifies that there are only minor differences, you can also choose to manually make the updates.
If the cluster name in a database is different that the name on the local node, a synchronization will overwrite the cluster name on the remote (slave element).
A Data Migrate operation synchronizes the system data from the master controller to the slave controllers with the data overwrite and merge options set to the recommended defaults. For resilient peer controllers, it also writes the user and device data from the resilient devices on the master controller to the resilient devices on the slave controllers
The Data Repair operation overwrites all the shared data, including the user and device data, on the slave controller with the shared data from the master controller.
