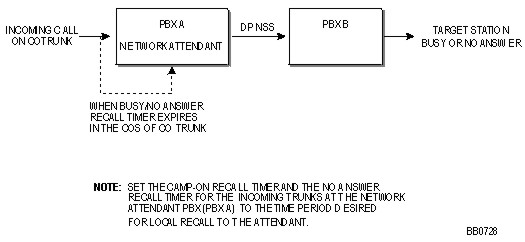
When an attendant extends an external trunk call to any station in the network the call will recall the attendant
if the call is not answered before the No Answer Recall Timer expires, or
if the caller camps on to the busy station and the Camp-on Recall Timer expires.
This feature displays the name and number of the station that the call is being recalled from, on the attendant console. There are two types of network attendant recall as shown in Local Network Attendant Recall and Remote Network Attendant Recall.
Local Network Attendant Recall

Remote Network Attendant Recall
External trunk calls that are extended over MSDN trunks to stations on other systems in the network will recall the network attendant. The attendant console displays the station's name and number.
If the station forwards the external trunk call to another destination, the call can recall the attendant. The recall displays the name and number of the station that the attendant initially extended the call to.
A call originating from a station in the network will not recall the attendant.
To have full network attendant recall functionality across the network, all the systems must be Mitel systems.
Local Network Attendant Recall Conditions (see Local Network Attendant Recall)
Both the network attendant system (PBX A) and the destination system (PBX B) must be Mitel systems in order for calls to recall. Recalls will display the name and number of the station.
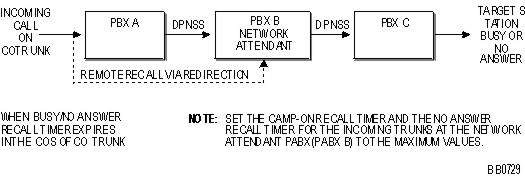
Remote Network Attendant Recall Conditions (refer to Remote attendant recall)
PBX A must support redirection for calls to recall the network attendant on PBX B.
PBX A, PBX B, and PBX C must be Mitel systems for the station name to be displayed on the attendant console.
If PBX A is a non-Mitel system that supports redirection, the call will recall but the station name will not be displayed on the attendant console.
Set the Call Hold Timer (10-600 s) in the class of service of the incoming trunk at the network attendant system. A trunk call placed on hold at the console will recall the attendant when this timer expires.
Local Network Attendant Recall Programming (refer to Local Network Attendant Recall)
For incoming external trunks at the network attendant system, set the Camp-on Recall Timer and the No Answer Recall Timer to the time period desired for local recall to the network attendant.
Remote Network Attendant Recall Programming (refer to Remote attendant recall)
For incoming DPNSS trunks at the network attendant system, set the Camp-on Recall Timer and the No Answer Recall Timer to the maximum values (180 seconds and 125 seconds respectively). Using the maximum values ensures that the recall timers for the central office trunks at the originating system expire first, causing the call to be redirected to the network attendant. If these options are not set to the maximum values, the call could recall the attendant locally and the name and number would not be displayed.
When the attendant answers a recall, the name and number of the station that the call is being recalled from appears in the attendant console display.
The attendant can press the REDIAL DEST key or RING AGAIN softkey to redial the call if the leading digits of the recall (as shown in the DEST display) are the same as the leading digits that the attendant originally dialed to extend the call. If the leading digits are not the same, pressing the REDIAL DEST key or RING AGAIN softkey places the call to the wrong station or results in error tone.
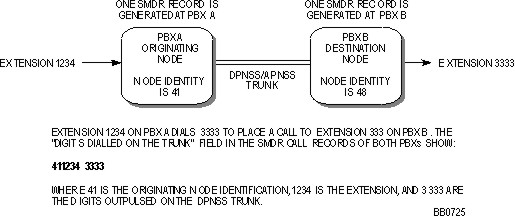
This feature allows an SMDR report to trace the path of a DPNSS or APNSS call through a network, by recording information in the "Digits Dialed on the Trunk" field of an SMDR record.
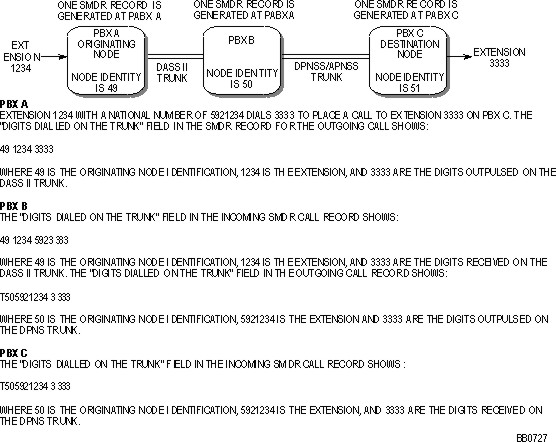
For DPNSS/APNSS trunk calls within the network the originating node identification, the extension number of the calling station, and the actual digits dialed are recorded.
DPNSS/APNSS Trunk Calls Within the Network
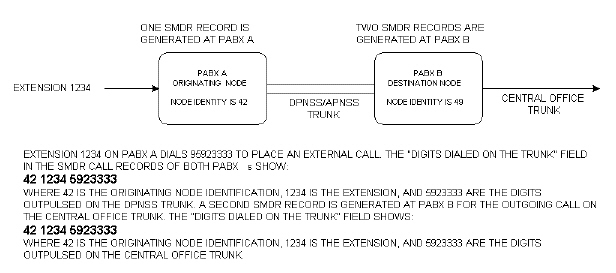
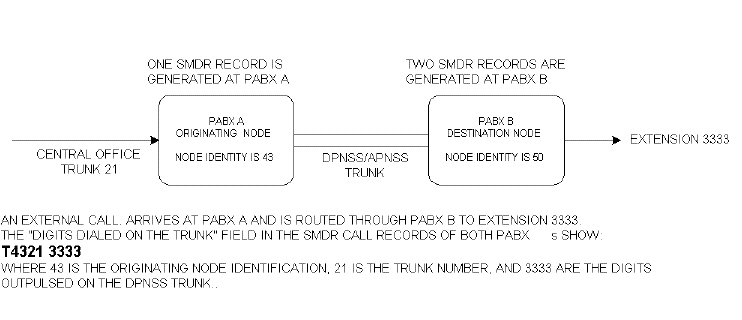
For outgoing DPNSS/APNSS trunk calls that originate internally, the originating node identification, the extension number of the calling station, and the actual digits dialed are recorded.
Outgoing DPNSS/APNSS Trunk Calls that Originate Internally
For outgoing DPNSS/APNSS trunk calls that do not originate internally (e.g. trunk to DPNSS to trunk), a "T" followed by the originating node identification, the trunk number, and the actual digits dialed are recorded.
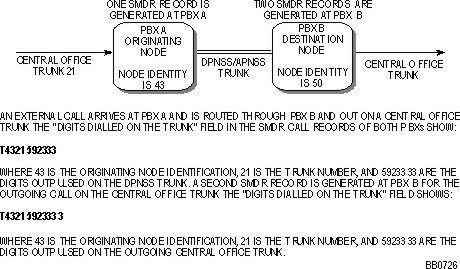
For incoming trunk calls, a "T" followed by the originating node identification, the trunk number, and the actual digits dialed are recorded.
For DASS II trunk calls within the network, a "T" followed by the originating node identification, and the digits of the national number are recorded.
Digit modification at any node in the network call path may affect the called party's number in SMDR records.
If any digit of the originating node ID or extension number is not a telephony digit (i.e., 0-9, *, #) an * will be substituted.
To have the originating node ID of incoming DPNSS/APNSS trunk calls appear in the SMDR records, you must set the OLI Node ID Format for Incoming Trunk Calls option in the SMDR Options form to "Yes".
Also see SMDR conditions.
In the SMDR Options form, set the following options to "Yes":
Network Format
Report Incoming Calls
Report Outgoing Calls
OLI Node ID Format for Incoming Trunk Calls
See Station Message Detail Recording for operation.
This feature allows forwarding party information such as; node identification, directory number, call forward type information, and the forwarding party's name to be sent across a DPNSS network. It also allows DPNSS callback message cancelation for voice mail usage only.
The voice mail subscriber can implement voice mail on a remote node by entering the node identification (optional) and voice mail hunt group pilot number as the call forward number. The voice mail port can be used as a destination for all types of call forwarding i.e., always, busy, no answer.
None.
Enter the subscriber's node identification (optional) and the voice mail hunt group pilot number as the call forwarding information on the subscriber's set. See Call Forward and Call Rerouting.
This feature decodes the forwarding party information received over the DPNSS trunk for the purpose of:
displaying node ID and extension numbers on voice mail sets,
outpulsing the node ID and extension number to voice mail ports with the ONS interface.
Note: Uniform numbering plans do not require node IDs.
None.
Enter the subscriber's node ID (optional) and extension number, as the subscriber's mailbox number, into the voice mail database.
Note: Some voice mail systems have a defined maximum mailbox digit length. Consideration must be given to determine if node ID is to be used.
When a call is received that contains the forwarding party information, the information is scanned for the call forward type, the subscriber's node ID (optional) and the extension number. If the call is destined for a voice mail port, then the call forward type is translated into the appropriate call type in the trunk's call record; the node ID and extension number are written to the remote party block of the DPNSS trunk.
Voice mail ports for a display set will show:
|
|
With Node ID |
Without Node ID |
|
Call Forward Always |
CFFM: 5601234 |
CFFM: 1234 |
|
Call Forward Busy |
CFB: 5601234 |
CFB: 1234 |
|
Call Forward No Answer |
CFNA: 5601234 |
CFNA: 1234 |
For voice mail ports with an ONS interface, the node ID (optional) and extension number will be outpulsed to the port when the call is answered. If the network does not employ node IDs, then only the extension number is displayed or outpulsed.
The voice mail system will activate or deactivate the message waiting indications on the subscriber's set once a voice message has been recorded for a particular subscriber or the subscriber has received all the recorded messages. The voice mail port controls the message waiting indications by using the message waiting activate and deactivate Feature Access codes. The voice mail port dials the Feature Access code and the subscriber's node ID (if required) and directory number.
The system determines where the extension resides, such as on a main or remote site. A DPNSS message will be sent to the remote sites to indicate a callback message from the voice mail hunt group.
See Messaging - Dialed in the Features Reference.
'Call me back' messages on the remote sites cancel after the 'SS4 Callback Message Cancel Timer' in the System Options form times out. This timer is set at each of the remote sites. The voice processor may be programmed to refresh message indications at preset intervals.
'Call me back' messages can be erased from display sets if the 'Multiline Set Voice Mail Callback Message Erasure Allowed' is enabled in the sets class of service.
See Voice Mail - ONS Interface and Voice Mail - E&M Interface.
Set the voice processor to 'message
waiting
For remote sites set the 'SS4 Callback Message Cancel Timer' (1-255 hrs) in the System Options form.
Display and message key sets are able to read messages set by voice mail through the use of the existing callback messaging interface. The subscriber can place a call back to the voice mail hunt group by pressing the appropriate key. (See Messaging - Callback.)
Subscriber's on remote nodes are able to erase the callback messages without retrieving their voice messages, since the 'Erase' or equivalent softkey is presented.
None.
See Messaging - Callback.
See Messaging - Callback.
The override feature allows a caller who encounters a Busy or Do Not Disturb condition, to enter the conversation or override the Do Not Disturb condition. Before the caller enters a conversation, both of the parties in the existing call receive warning tone. This tone is repeated at regular intervals while the overriding party is connected.
The overriding station cannot manipulate the existing call in any manner.
The executive busy override option must be enabled in the station's class of service for the feature to be effective.
A station on hold cannot be overridden.
A station with a call on consultation hold cannot be overridden.
A conversation which contains a station with the busy override security COS cannot be overridden.
A call in which either station has set up call privacy cannot be overridden.
A conference cannot be overridden via an MSDN/DPNSS trunk.
A call in which one member is a non-MSDN/DPNSS trunk cannot be overridden.
A busy hunt group cannot be overridden.
A station which is receiving a tone or is in a dialing situation cannot be overridden.
Class Of Service Options form: The executive busy override option must be enabled for each station that has the ability to initiate override.
Feature Access Codes form: Assign a single digit access code to override. First digit conflict between override and other Feature Access codes is permitted with the exception of callback and camp-on.
See Override in the Features Reference.
